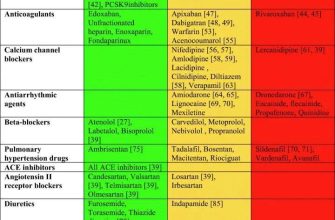
Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements. This includes prescription drugs, even if you only take them occasionally. Cephalexin can interact with certain medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects.
Antacids and other medications affecting stomach acid:
Taking cephalexin with antacids or medications that reduce stomach acid can decrease cephalexin absorption. Ideally, separate the administration of cephalexin from these medications by at least two hours. Your doctor can provide tailored advice based on your specific medications and health condition.
Warfarin:
Cephalexin may increase the effects of warfarin (a blood thinner), potentially leading to an increased risk of bleeding. Close monitoring of your INR (International Normalized Ratio) is crucial if you’re on warfarin. Your physician might need to adjust your warfarin dosage. Regular blood tests will be necessary.
Oral contraceptives:
Some reports suggest cephalexin might reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives. While further research is needed, discuss this potential interaction with your doctor, especially if you are concerned about unplanned pregnancy. They might recommend alternative birth control methods during cephalexin treatment.
Remember, this information is not exhaustive. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance regarding medication interactions and potential side effects. They can assess your individual risk factors and provide the best advice for your health.